By studying a pair of genetically identical twins, NASA discovered some of the strange things that happen when bodies experience zero-gravity.
Wikimedia Commons
The International Space Station
When Japanese astronaut Norishige Kanai sent his Twitter report back down to Earth after just three weeks in orbit, his tweet contained a lofty claim.
“Today there is a serious report…” he said, sending his tweet from the International Space Station. “I had physical measurements since I got to space… [with] heights up to 9 centimeters!”
That’s right, Kanai claimed that in the short three weeks since he’d been launched into space, he’d grown about three and a half inches. Unfortunately for Kanai, his claims have since been branded “fake news,” as his measurements actually reveal that he’d only grown about two centimeters.
However, despite the outlandish claim, there is a bit of truth to them – astronauts who spend extended time in space typically come back to Earth slightly taller than they were when they left.
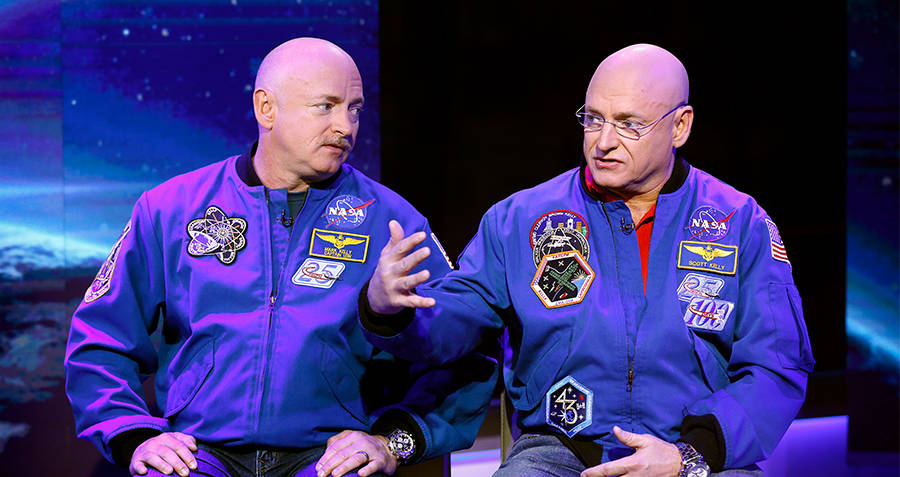

Getty ImagesAstronaut twins Scott and Mark Kelly
NASA has been studying this height change and other physiological changes that space travel inflicts on the body, by observing the Kelly twins for the past three years.
NASA began the study in 2015, when Scott Kelly was assigned to a year-long mission in space. After he got his assignment, he approached NASA with an idea. Send him on his regularly scheduled mission, but observe his genetically identical twin while he was away to see what effects space travel had on the body.
“I asked the scientists if anyone had any interest in doing any comparative studies on Mark and I, considering he’s also an astronaut and they had a lot of data on him for a really long time,” Scott said. “And they went back over the next couple of weeks and talked about it and decided that there was in fact an interest and asked us if we would be participants.”
“After talking to NASA about this, Scott came to me and said, ‘Would you be willing to do this?'” said Mark, who had been working for NASA as part of the space program for the past 15 years. “I said, ‘absolutely,’ to do whatever they’d like. They don’t even have to pay me.”
NASA, of course, did have to pay him, despite his protests – and they eventually agreed to a minimum wage of $10.50 an hour.
Scott’s original mission was to spend 340 days between 2015 and 2016 on the International Space Station. Now, however, there was another phase. His brother, Mark, had been recruited to stay on Earth to serve as a control subject. The two brothers heights, weights, and other physical characteristics were all recorded before Scott’s journey. Additionally, NASA collected biological samples such as blood and saliva, for comparison.
Then, Scott was launched into space, and the experiment officially began.
After spending almost a full year at the ISS, Scott returned to earth with a bit of a surprise – after being measured, he found he was a full two inches taller than he had been before his trip.
What caused the growth? Gravity, of course. Well, actually, a lack thereof.

Getty Images
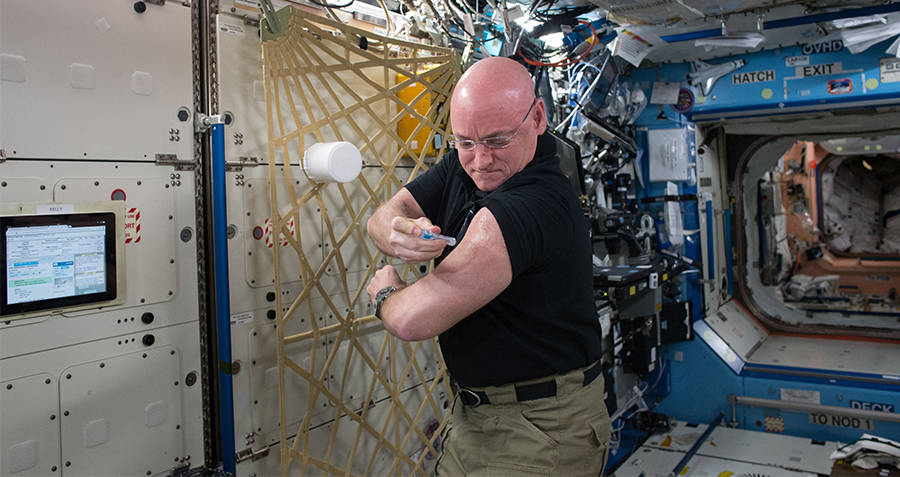
Scott Kelly giving himself a flu shot on the ISS, in order to observe the effects of gravity on the immune system.
According to NASA, spending extended time in a zero-gravity environment, like the International Space Station, can cause the spine to stretch. The space in between the vertebrae – usually pushed together by gravity – is allowed to expand without the constant pressure. With the expansion, the average person grows anywhere from a few centimeters to a few inches.
In addition to being a little bit taller, NASA scientists found a few other surprising changes caused by zero-gravity living.
One of the studies done on the twins’ DNA showed that space actually changed Scott’s. The telomeres, structures on DNA strands that indicate how old you are, were longer on Scott’s DNA than Mark’s. According to Scott, that’s actually the opposite of what NASA assumed would happen. Due to the levels of radiation in space, NASA assumed that the telomeres would shrink, but in fact, they grew.
Unfortunately, those hoping that NASA’s uncovered a fountain of youth or a quick way to gain a few inches will be sorely disappointed. There’s no indication that Scott’s telomere’s really affected his age, and of course, once reintroduced to a gravity-laden environment he shrank right back to his original height.
Next, check out these amazing photos of Scott Kelly in space. Then, read the chilling stories of the only people known to have died in space.




