Before they died out roughly 1,000 years ago, elephant birds could grow up to 10 feet tall and laid the largest eggs ever documented.
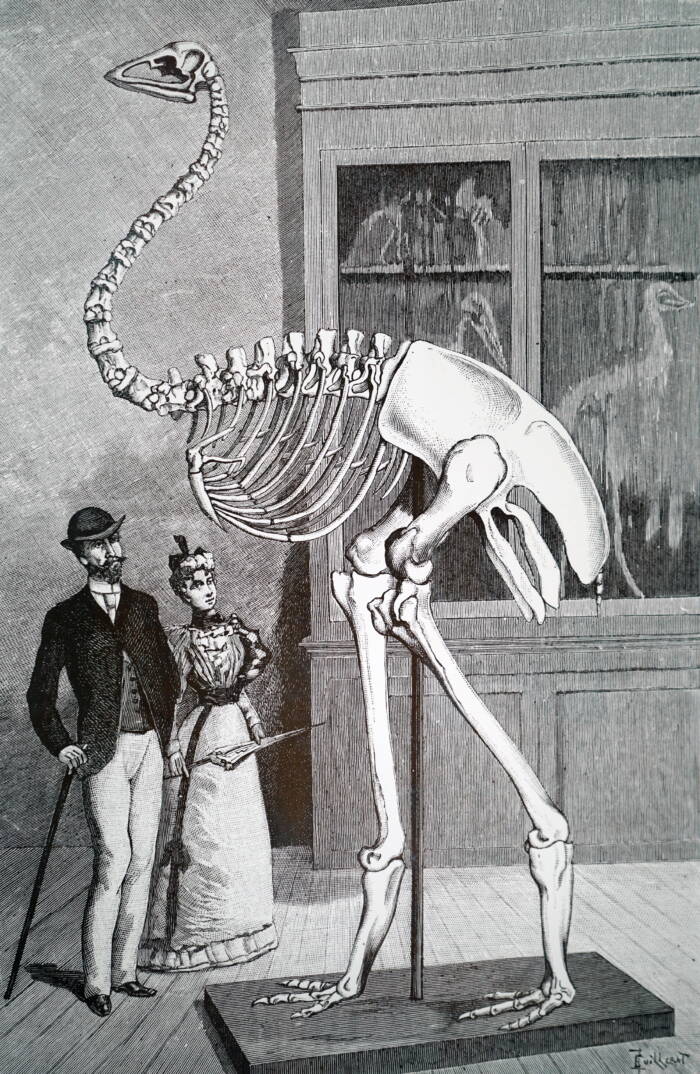
World History ArchiveAn engraving of the elephant bird from the 19th century.
Before it went extinct 1,000 years ago, the elephant bird of Madagascar was certainly a sight to behold. In fact, one species of this flightless bird is widely believed to be the largest bird that ever lived.
Though long the stuff of legends — these bird may have inspired stories of the mythical roc (or rukh) creature — elephant birds were very real. That said, they’ve long been something of a mystery for scientists. It’s only in recent years that researchers have suggested that elephant birds of the Aepyornithidae family include four distinct species: Mulleornis modestus, Aepyornis hildebrandti, Aepyornis maximus, and Vorombe titan.
Driven to extinction shortly after humans settled in Madagascar, the story of this colossal bird is still being told.
The Elephant Bird Of Madagascar
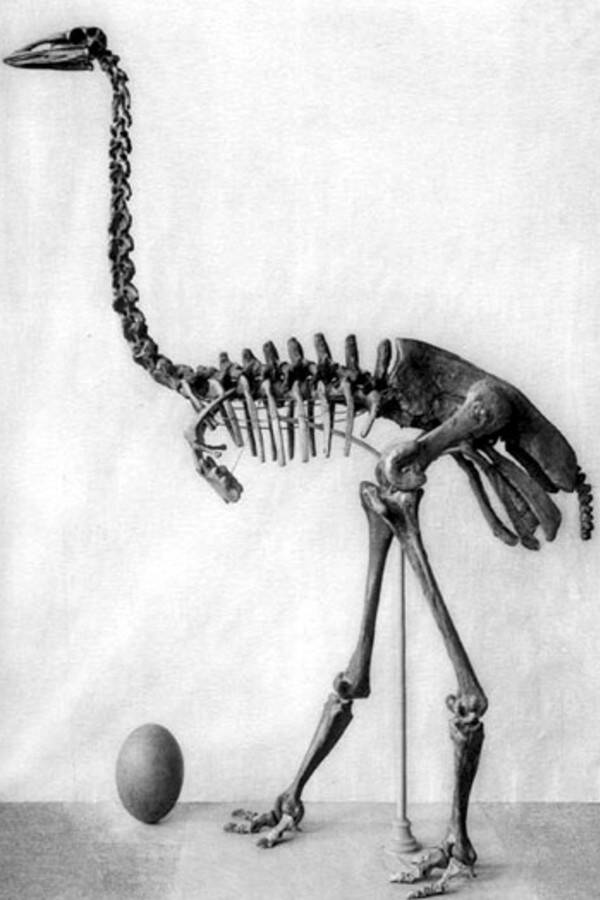
Public DomainThe skeleton of Aepyornis maximus , one of the elephant bird species.
Long before the elephant bird was scientifically studied, it existed in myth. Explorers in the 13th and 14th centuries, including Ibn Battuta and Marco Polo, relayed stories of a giant bird that lived near Madagascar, which they claimed was the mythical creature known as roc or rukh. As late as the 19th century, the British explorer and novelist William Winwood Reade similarly claimed that, “The existence of the Roc… is now proved by the discovery of an immense egg in a semi-fossil state in Madagascar.”
In fact, this mythical bird creature — and its eggs — was the elephant bird, a real creature that went extinct around 1000 to 1200 C.E.
Elephant bird fossils are abundant — so abundant that researchers originally believed that there were as many as 15 species of these massive creatures. However, recent research suggests that there were just four species of these birds split across three genera: Mulleornis modestus, Aepyornis hildebrandti, Aepyornis maximus, and Vorombe titan.
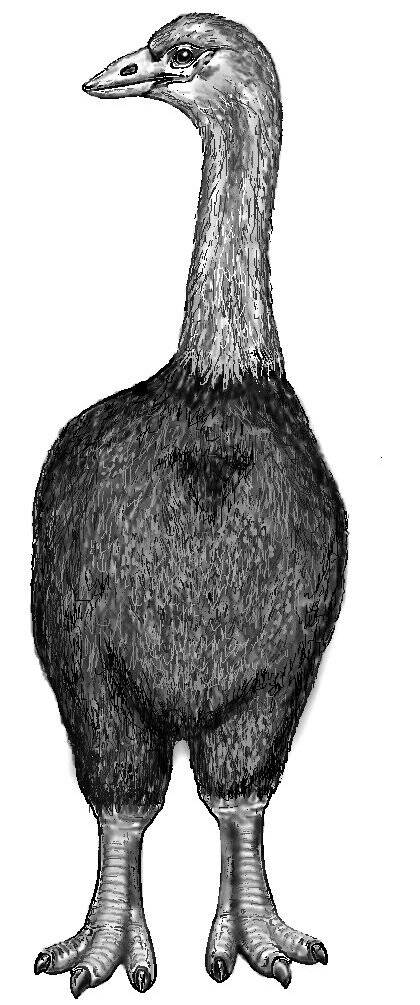
Acrocynus/Wikimedia CommonsA depiction of how elephant birds looked. Though they resembled ostriches, they were more closely related to kiwis.
These birds had conical beaks, stubby legs, three-toed feet, and small wings that were useless for flying. Though they resemble ostriches, they’re more closely related to kiwis, and they likely lived in forests and ate plants.
But the most impressive thing about elephant birds were their size.
One Of The Largest Birds In The World
Though myths about the elephant bird long abounded, they were first given a scientific description by French zoologist Isidore Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire in 1851. Saint-Hilaire called the birds Aepyornis maximus, or “Greatest high-bird.” According to the science magazine Capeia, Saint-Hilaire also noted that elephant bird eggs were the largest of any documented species.
These eggs could be as tall as 13 inches and hold roughly two gallons of liquid, or the equivalent of about 150 chicken eggs. And indeed, the size of the elephant bird matched their massive eggs. Many stood 10 feet tall and weighed around 1,000 pounds. But the largest of the species is believed to be Vorombe titan.
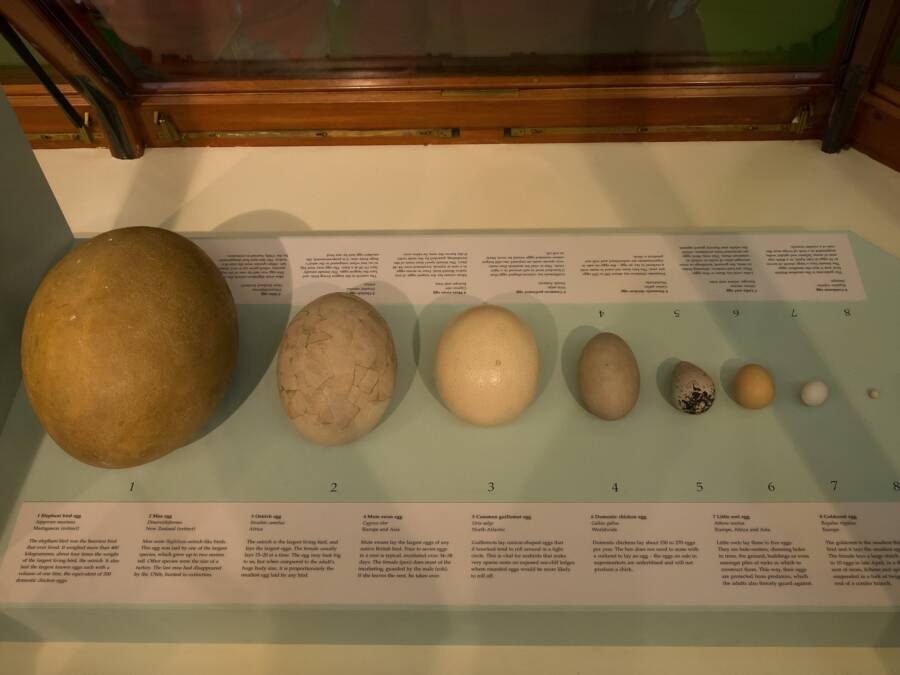

Denis Bourez/Wikimedia CommonsAn elephant bird egg, far left, compared to eggs from other birds.
Originally identified as the species Aepyornis titan in 1894, recent studies suggest that Vorombe titan belongs to a distinct genus. (Vorombe is Malagasy for “big bird.”) While its cousins may grow up to 1,000 pounds, researchers believe that V. titan could have been as much as 1,700 pounds.
If so, that would make V. titan the largest bird ever documented — even larger than the Dromornis stirtoni, a flightless bird from Australia that went extinct 20,000 years ago and weighed 1,100 pounds.
In short, these were massive — but gentle — land creatures who thrived on a tiny island off the coast of Africa for thousands of years.
So, how did these giant bird go extinct?
The Extinction Of The World’s Largest Bird
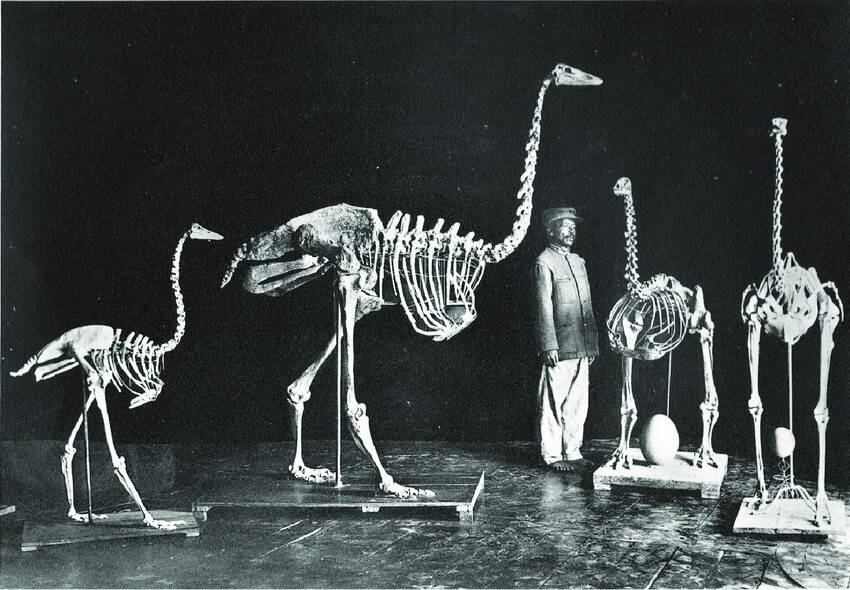

Public DomainAn elephant bird skeleton displayed alongside other bird skeletons. To date, the elephant bird is considered the largest bird to ever walk the earth.
Simply put — and perhaps unsurprisingly — it was most likely human behavior that caused the mighty elephant bird to go extinct.
As the BBC reported in 2018, these giant birds and early humans seemingly coexisted on Madagascar for centuries. However, human activity eventually chipped away at the elephant bird population.
Not only did humans hunt and butcher the birds for their meat, but they also stole the birds’ eggs. Early humans might have used the eggs for food — just one giant egg could easily feed an entire human family — but it’s also possible that they used them to store rum or as bowls.
This pressure on elephant birds, combined with climate change and changes to their environment, ultimately led to their extinction roughly 1,000 years ago. By 1200 C.E., the birds had died out completely, leaving behind only myths — and plenty of fossilized eggs and bones.
But could new technology bring the extinct bird back to life?
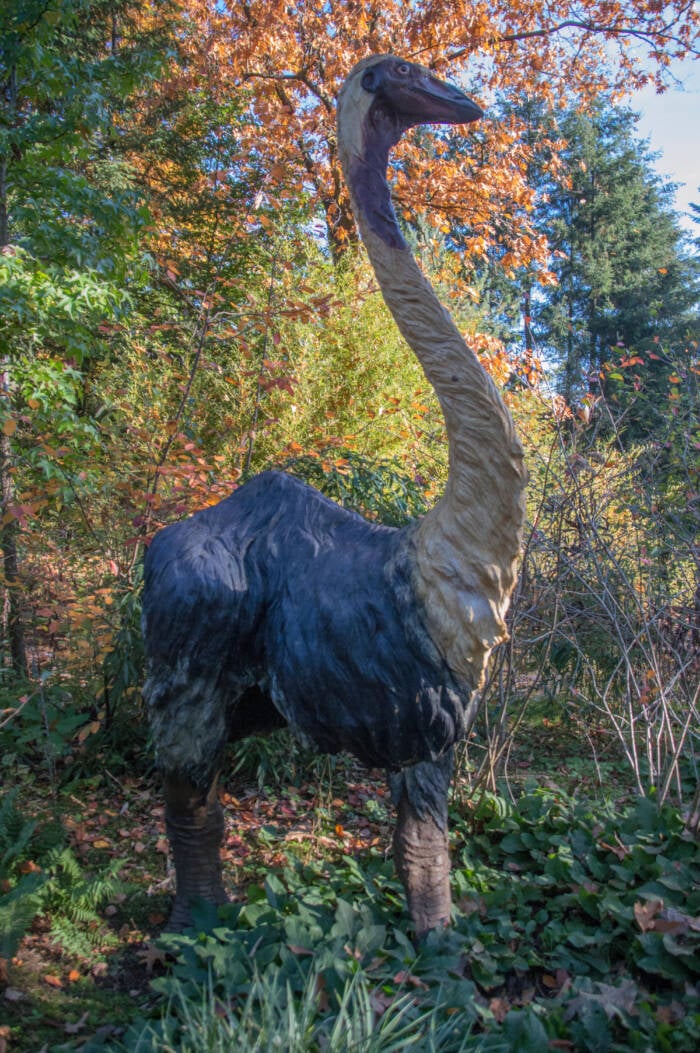

Robert vant Hoenderdaal / Alamy Stock PhotoA model of an elephant bird.
In recent years, scientists have toyed with the idea of de-extinction, or the idea of bringing extinct animals back to life. Animals like the dodo, the Tasmanian tiger, and the woolly mammoth have all been proposed as possible de-extinction candidates.
Though there’s currently no de-extinction project focused on the elephant bird, this extinct species could be a good candidate. Little DNA has been found in their bones, which have been bleached by the Madagascar sun, but fossilized elephant bird eggs are a rich source of DNA.
As such, perhaps the story of the elephant bird isn’t quite over. Though the last of these creatures went extinct some 1,000 years ago, they left behind a rich source of DNA in their eggs. As humans grapple with the idea of bringing animals back from the dead, perhaps the elephant bird — or some version of it — can be revived. If that happens, then maybe these gigantic birds will one day wander through the forests of Madagascar once again.
Now that you’ve read all about the elephant bird, discover the story of Dracula parrot, the most “Goth” bird on the face of the planet. Then, learn all about the shoebill, the bird that can decapitate crocodiles.





