During the early 14th century, King Mansa Musa I reigned over Mali — and amassed enormous wealth that remains jaw-dropping to this day.
Imagine how much money the richest person in history would have. Now add a couple hundred billion, and you’ve probably gotten closer to how much wealth Mansa Musa had during the 14th century.
As the king of the Mali Empire in West Africa, Musa first came to power in 1312. At that point, the kingdom was already prosperous.
Wikimedia CommonsA 14th-century depiction of Mansa Musa, who is believed to have been the richest person in history.
But under the rule of Musa, Mali became even more wealthy. Taking advantage of the region’s natural resources — like gold and salt — Musa expanded his empire throughout several territories and made a big impression along the way.
Economists have determined that the West African emperor’s vast fortune most likely positions him as the richest person in history. But just how much money did he have? And what did he do with it?
How Mansa Musa Became The Richest Man In History

Wikimedia CommonsMansa Musa’s net worth is believed to have been the equivalent of $400 billion.
Mansa Musa came to reign over the Mali Empire through somewhat strange means.
It all started when the former emperor, Abubakari II, deputized Musa to temporarily assume his role. An “on-call” emperor was a common feature throughout the history of this empire. It was somewhat comparable to the modern-day role of a vice president — as the person would be expected to step in on a full-time basis if anything happened to the main emperor.
In a twist of fate, Musa would indeed need to step in. Abubakari set out to explore the far side of the Atlantic Ocean one day — and never returned. And so Musa became Mansa Musa (Mansa means “king”) and inherited the throne in 1312, becoming the ninth mansa of the Mali Empire. But Musa hadn’t been plucked from obscurity to lead. His great-uncle was Sundiata Keita, who had founded the Mali Empire.
As many a late-night infomercial will tell you, there are lots of ways to attain wealth. Musa earned his fortune primarily through trading gold and salt, which were found in abundance in West Africa at the time. He used much of his wealth to strengthen important cultural centers, especially Timbuktu.
But despite his massive success, Musa was not very well known beyond the region he ruled — until he journeyed outside of Africa. A devout Muslim, Musa was determined to make his pilgrimage to Mecca (also known as a Hajj) in 1324. And with that, the rest of the world would soon know his name.
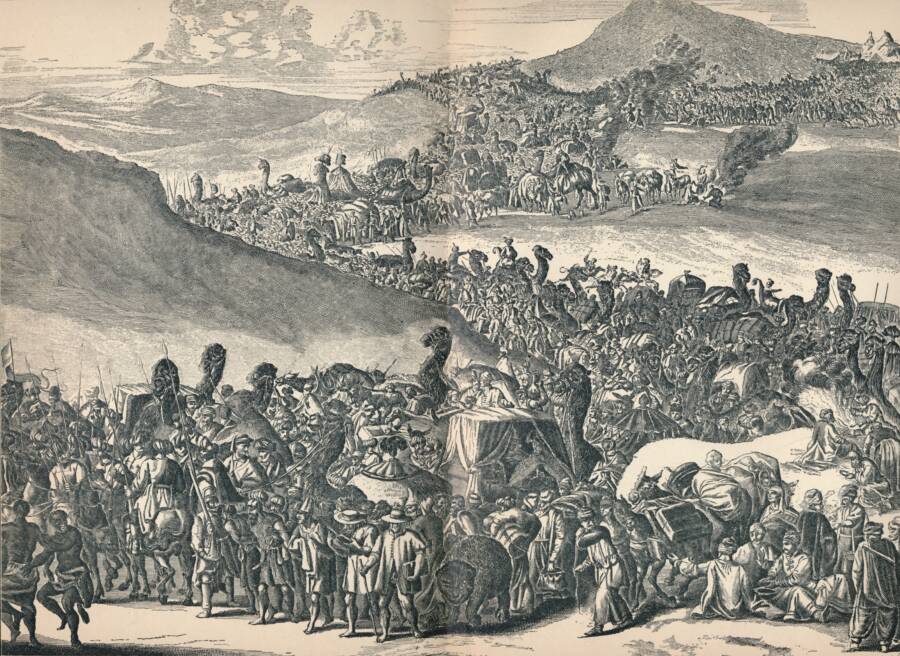

Print Collector/Getty Images“Mansa Musa on His Way to Mecca,” as depicted by a European artist in 1903.
Going on a pilgrimage to Mecca is an important part of Islam to this day. And for Musa, it was no small feat. He would have to travel 4,000 miles from his empire to get there. As a rich and powerful emperor, he certainly could not go alone. Musa embarked on his pilgrimage accompanied by a total of 60,000 people — a mix of servants, soldiers, and supporters.
Musa’s servants weren’t dressed in rags, as one might expect. Instead, they were wrapped in Persian silks and carried gold staffs.
The world quickly began to take notice of Musa’s convoy of people, horses, and camels. Not only was Musa’s caravan impossible to miss, but he was also buying as many goods as he could find — and giving away gold to random peasants on the street. As Musa passed through Cairo, Medina, and finally to Mecca, he left the streets basically littered with gold.
But sometimes, Musa left an oversized wake. In Cairo, the emperor gave away so much gold that he actually messed up the economy for a while. There was so much of it that the value went down.
The disruption eventually evened out, in part because Mansa Musa began borrowing from lenders in Cairo (despite the high-interest rate). And by that point, the king almost single-handedly controlled the price of gold in the Mediterranean region. However, it did take over a decade for Cairo’s economy to fully recover from Mansa Musa’s golden touch.
There’s no question that Musa’s pilgrimage to Mecca would help cement his place in history. But at the time, he simply saw it as a necessary journey to honor his faith — and a way to expand his growing kingdom. During that historic trip, he acquired the territory of Gao. And by the end of his reign, Musa would extend his empire to include present-day Senegal, Gambia, Guinea, Niger, Nigeria, Chad, and Mauritania — in addition to Mali.
The Lasting Contributions Of Mansa Musa’s Wealth
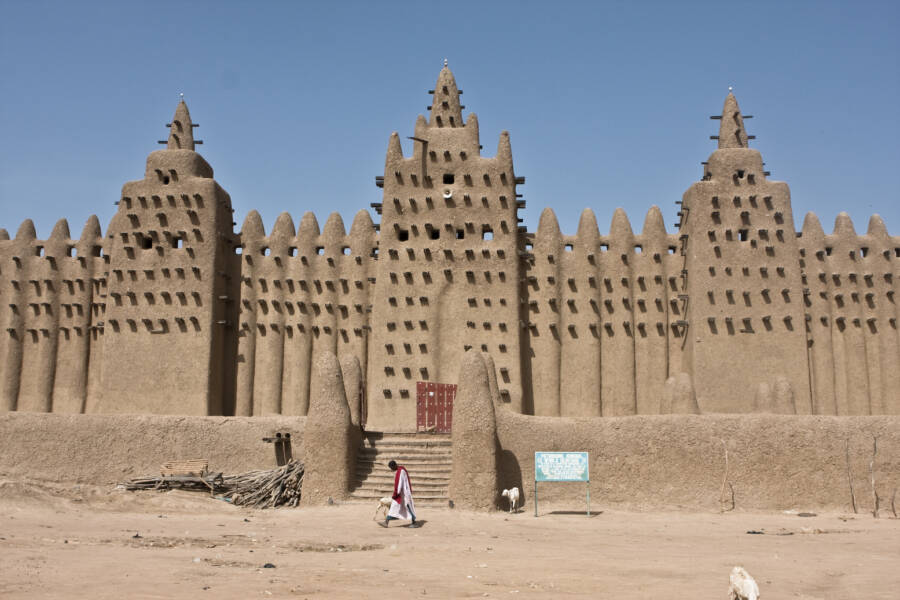

Wikimedia CommonsMansa Musa used part of his fortune to build the Djinguereber Mosque, which still stands today.
So what did Mansa Musa do with all the money, aside from giving away gold to random people on the street and using it to buy souvenirs?
Ultimately, he used most of it to build a great number of mosques (legend says he built one every Friday during his reign), the most famous of which is the Djinguereber Mosque. He also commissioned several universities throughout the kingdom. Many of these historic buildings — both the schools and the mosques — are still standing today, some 700 years later.
While Mansa Musa was alive, his investment in Islamic education in Mali drew scores of Muslim scholars, poets, and artisans to his empire. They congregated in Timbuktu, which quickly became known as one of the most prominent cities in the Islamic world.
In addition, Musa quite literally put himself, and his empire, on the map. His caravan during his Mecca pilgrimage had attracted so much attention that Europeans — who were thousands of miles away — heard about the trip.
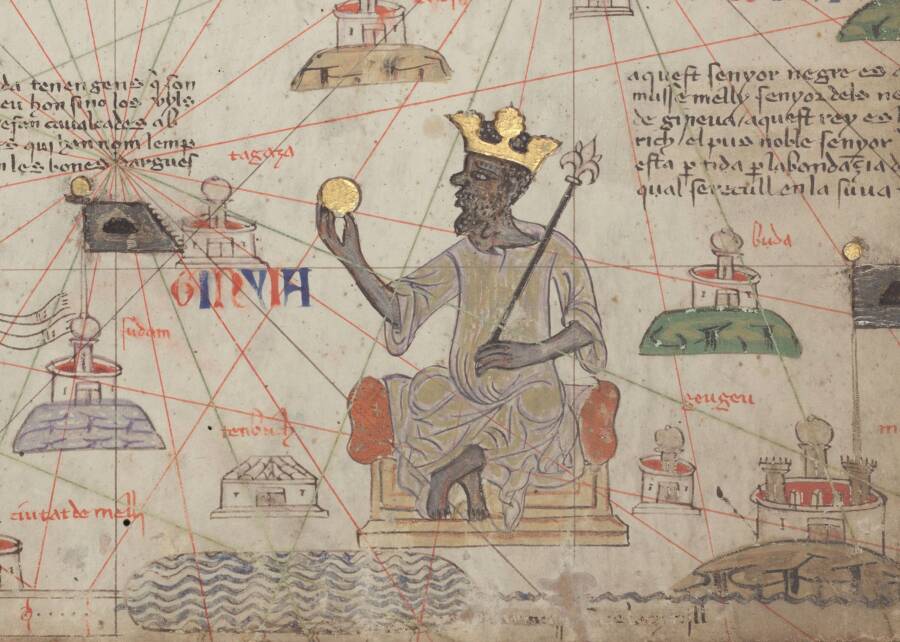
During the late 14th century, the Spanish cartographer Abraham Cresques drew some famous maps that included Musa’s likeness. In these images, the emperor wears a crown, grips a scepter, and holds up a nugget of gold.
This depiction of a wealthy king created something of a fantasy for people in Europe. At the time, many European countries were struggling through the bubonic plague, civil wars, and economic hardship. The image of a prosperous Timbuktu — and massive amounts of gold — wove an enchanting tapestry in the European imagination.
Ultimately, Musa ruled the Mali Empire for about 20 years. During that time, he extended the reach of his trade ports significantly and became one of the most powerful rulers of his day — and perhaps of all time.
He’s believed to have died in 1332, at which time his son inherited the throne.
Comprehending The Vast Wealth Of The Richest Person In History

Wikimedia CommonsAs of May 2021, Amazon founder Jeff Bezos is the richest man in the world. But Mansa Musa’s net worth likely dwarfed that of Bezos and other modern tycoons.
In the spirit of other wealthy people who ultimately become philanthropists, you might wonder how Mansa Musa stacks up against some contemporary billionaires, like Jeff Bezos, Elon Musk, Bill Gates, or John D. Rockefeller.
When adjusted for inflation, Mansa Musa’s net worth is believed to have been around $400 billion. The only American billionaire from modern history who even comes close to that amount is John D. Rockefeller, whom economists believe amassed a worth of around $336 billion.
But today’s billionaires don’t even get close to Musa’s wealth. As of May 2021, Bill Gates comes in far below Musa at $126 billion. Jeff Bezos and Elon Musk are a little closer. Bezos, currently the world’s richest person, is worth about $187 billion. Meanwhile, Musk has $156 billion to his name.
In other words, today’s richest people don’t even have half of Mansa Musa’s net worth that he accumulated as emperor all those centuries ago. This has led many experts to believe that Musa was the richest person in history. But to this day, many still struggle to comprehend the true size of his fortune.
“Contemporary accounts of Musa’s wealth are so breathless that it’s almost impossible to get a sense of just how wealthy and powerful he truly was,” said Rudolph Butch Ware, an associate professor of history at the University of California.
In the end, historians find Mansa Musa’s legacy rich not only because of how much money he had, but how he used it. And while his wealth may have been “indescribable,” he was clearly happy to share it with others.
After reading about Mansa Musa’s net worth and the story behind it, take a look at the richest people of all time. Then, learn about the “first Black woman millionaire” in the United States.





