Before Albert Einstein died in April 1955, he told his family he didn't want to be studied. But hours after he perished, a medical examiner stole his brain for research.
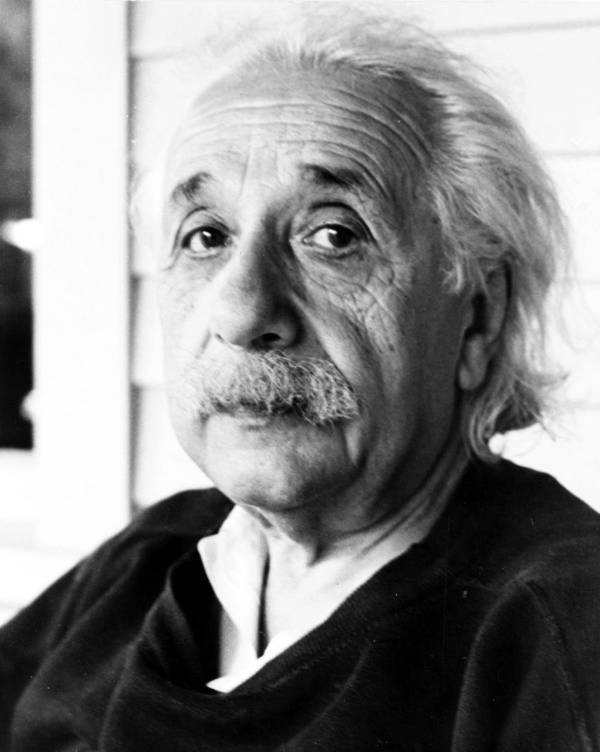

Wikimedia CommonsWhile analyzing Albert Einstein’s cause of death, an autopisiest famously removed the genius’s brain — without permission from his family.
When Albert Einstein was rushed to the hospital in 1955, he knew that his end was near. But the 76-year-old famed German physicist was ready, and he informed his doctors with all the clarity of a math equation that he would not like to receive medical attention.
“I want to go when I want,” he said. “It is tasteless to prolong life artificially. I have done my share, it is time to go. I will do it elegantly.”
When Albert Einstein died of an abdominal aortic aneurysm on April 18, 1955, he left behind an unparalleled legacy. The frizzy-haired scientist had become an icon of the 20th century, befriended Charlie Chaplin, escaped Nazi Germany as authoritarianism loomed, and pioneered an entirely new model of physics.
Einstein was so revered, in fact, that just hours after his death his inimitable brain was stolen from his corpse — and remained stashed away in a jar in a doctor’s home. Though his life has been dutifully chronicled, Albert Einstein’s death and the bizarre journey of his brain afterward deserve an equally meticulous look.
Before Albert Einstein Died, He Was The World’s Most Valuable Mind
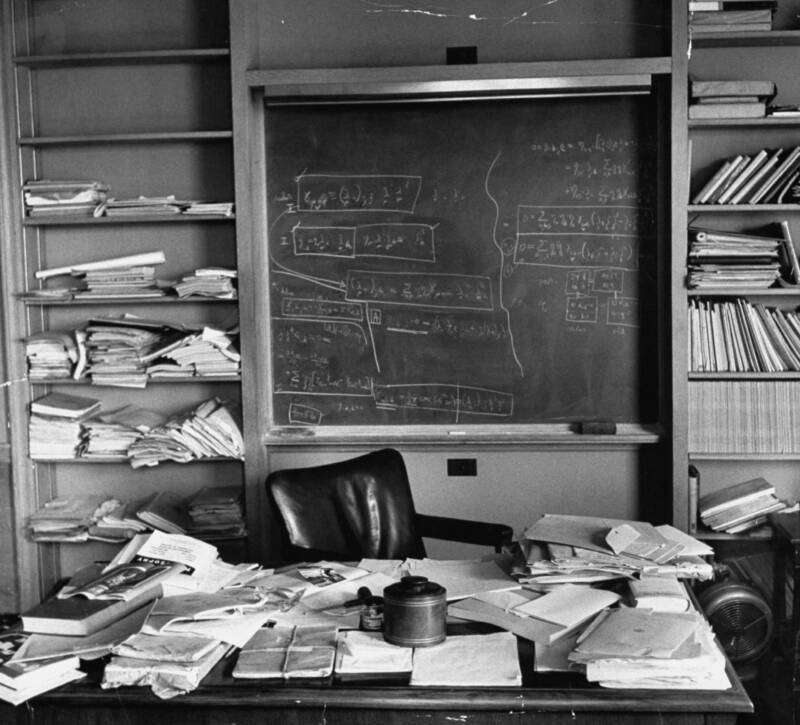

Ralph Morse/The LIFE Picture Collection/Getty ImagesBooks and equations litter Einstein’s study.
Einstein was born on March 14, 1879, in Ulm, Württemberg, Germany. Before he developed his theory of general relativity in 1915 and won the Nobel Peace Prize for Physics six years after that, Einstein was just another aimless middle-class Jew with secular parents.
As an adult, Einstein recalled two “wonders” that deeply affected him as a child. The first was his encounter with a compass when he was five years old. This birthed a lifelong fascination with the invisible forces of the universe. His second was the discovery of a geometry book when he was 12, which he adoringly called his “sacred little geometry book.”
Also around this time, Einstein’s teachers infamously told the restless youth that he would amount to nothing.

Wikimedia CommonsThe genius was a lifelong pipe smoker, and some believe this contributed to Albert Einstein’s cause of death.
Undeterred, Einstein’s curiosity about electricity and light grew stronger as he grew older, and in 1900, graduated from the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich, Switzerland. Despite his inquisitive nature and academic background, however, Einstein struggled to secure a research position.
After years of tutoring children, the father of a lifelong friend recommended Einstein for a position as a clerk in a patent office in Bern. The job provided the security Einstein needed to marry his long-term girlfriend, with whom he had two children. Meanwhile, Einstein continued to formulate theories about the universe in his spare time.
The physics community initially ignored him, but he garnered a reputation by attending conferences and international meetings. Finally, in 1915, he completed his general theory of relativity, and just like that, he was spirited around the globe as a lauded thinker, rubbing elbows with academics and Hollywood celebrities alike.
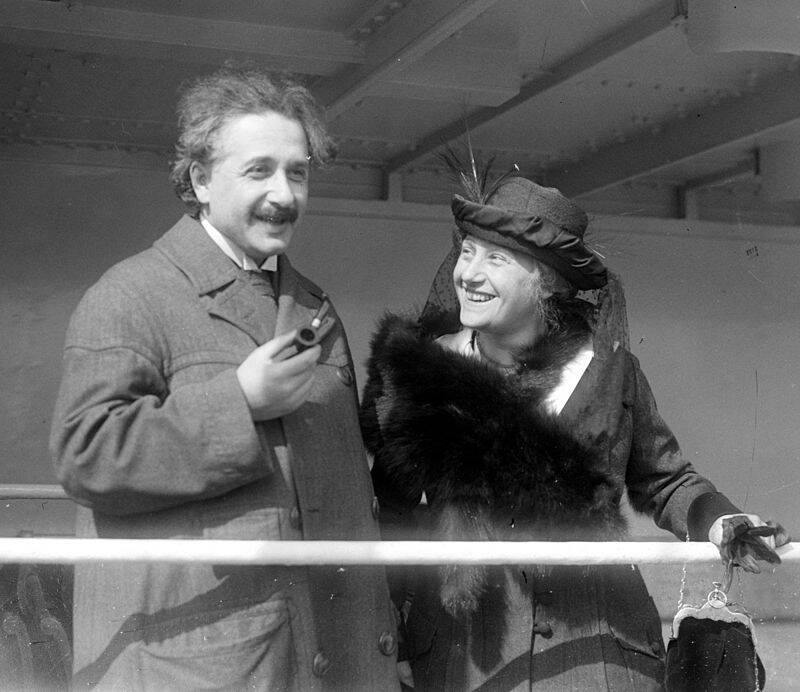

Wikimedia CommonsAlbert Einstein with his second wife, Elsa.
“The people applaud me because everybody understands me, and they applaud you because no one understands you,” Charlie Chaplin once told him. Einstein then reportedly asked him what all of this attention meant. Chaplin replied, “Nothing.”
When World War I hit, Einstein publicly opposed Germany’s nationalist fervor. And as World War II brewed, Einstein and his second wife Elsa Einstein emigrated to the United States to avoid persecution by the Nazis. By 1932, the strengthening Nazi movement had branded Einstein’s theories as “Jewish physics” and the country denounced his work.
The Institute for Advanced Study at Princeton University in New Jersey, however, welcomed Einstein. Here, he worked and pondered the world’s mysteries until his death two decades later.
The Causes Of Albert Einstein’s Death

Princeton UniversityPeople flocked to the Institute for Advanced Study at Princeton University upon hearing of Einstein’s death.
On his final day, Einstein was busy writing a speech for a television appearance commemorating the State of Israel’s seventh anniversary when he experienced an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), a condition during which the body’s main blood vessel (known as the aorta) becomes too large and bursts. Einstein had experienced a condition like this before and had it surgically repaired in 1948. But this time, he refused surgery.
When Albert Einstein died, some speculated that his cause of death could have been correlated with a case of syphilis. According to one doctor who was friends with the physicist and wrote about the death of Albert Einstein, AAA can be instigated by syphilis, a disease some thought that Einstein, who was “a strongly sexual person,” could have contracted.
However, no evidence of syphilis was found in Einstein’s body or brain in the autopsy that followed his death.
But Albert Einstein’s cause of death could have been exacerbated by another factor: his lifelong smoking habit. According to another study, men who smoked were 7.6 times more likely to experience a fatal AAA. Even though Einstein’s doctors had told him to quit smoking various times throughout his life, the genius rarely hung up the vice for long.
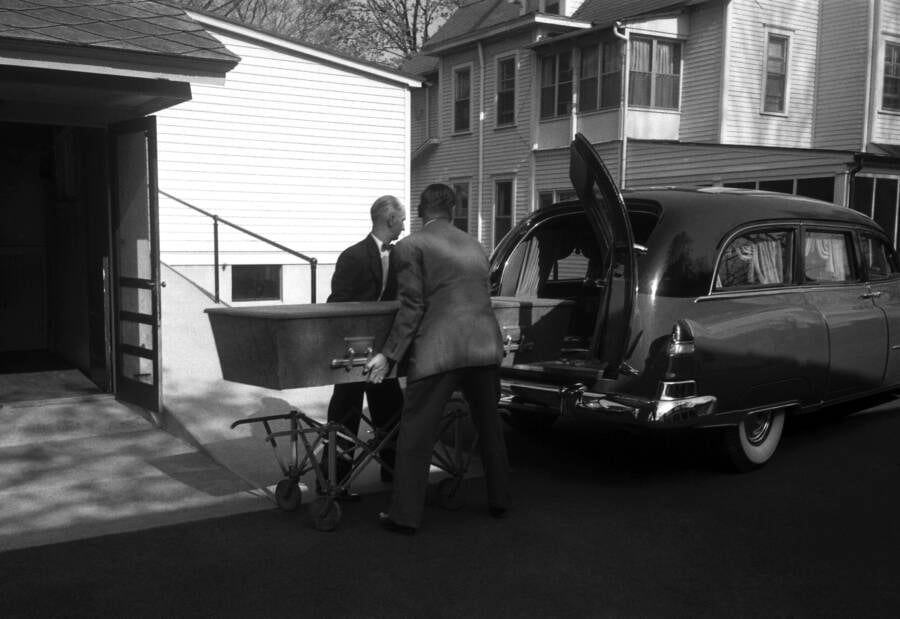

Ralph Morse/The LIFE Picture Collection/Getty ImagesThe body of Albert Einstein is loaded onto a hearse outside a Princeton, New Jersey funeral home. April 18, 1955.
On the day that Einstein passed, the Princeton Hospital was mobbed with journalists and mourners alike.
“It was chaos,” recalled LIFE magazine journalist Ralph Morse. Yet Morse managed to take some iconic photographs of the physicist’s home after Albert Einstein’s death. He captured shelves with sloppily piled books, equations scrawled on a chalkboard, and notes scattered across Einstein’s desk.
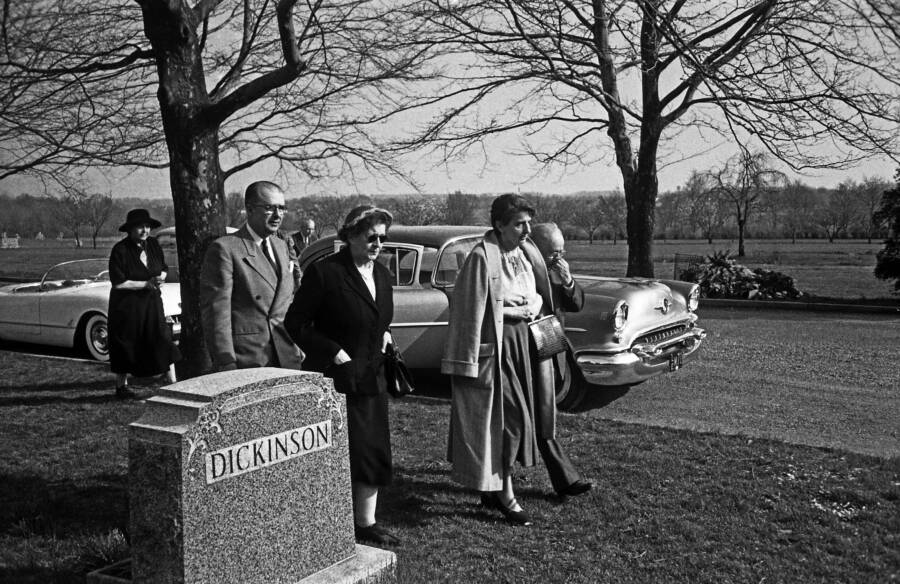

Ralph Morse/The LIFE Picture Collection/Getty ImagesEinstein’s son, Hans Albert Einstein (in light suit), and Einstein’s longtime secretary Helen Dukas (in light coat), at the Ewing Crematorium in Trenton, New Jersey the day after Einstein died.
But LIFE was forced to shelve Morse’s photographs because the physicist’s son, Hans Albert Einstein, pleaded with the magazine to respect his family’s privacy. Although LIFE respected the family’s wishes, not everyone involved in Albert Einstein’s death did.
His Brain Was Notoriously ‘Stolen’
Hours after he passed, the doctor who performed the autopsy on the corpse of one of the world’s most brilliant men removed his brain and took it home without the permission of Einstein’s family.
His name was Dr. Thomas Harvey, and he was convinced that Einstein’s brain needed to be studied as he was one of the most intelligent men in the world. Even though Einstein had written out instructions to be cremated upon death, his son Hans ultimately gave Dr. Harvey his blessing, as he evidently also believed in the importance of studying the mind of a genius.
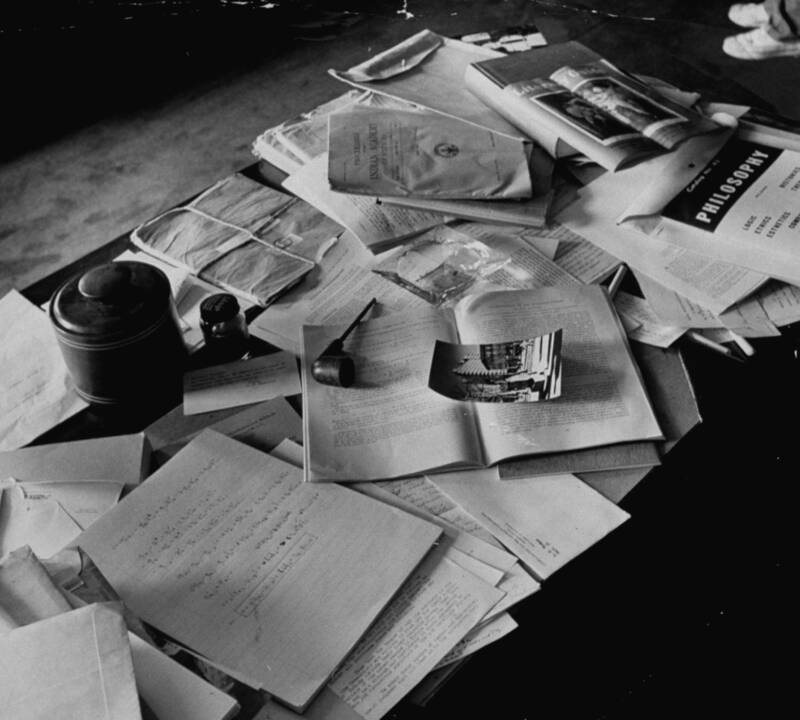

Ralph Morse/The LIFE Picture Collection/Getty ImagesAlbert Einstein’s cluttered office desk after he died.
Harvey meticulously photographed the brain and sliced it into 240 chunks, some of which he sent to other researchers, and one he tried to gift Einstein’s granddaughter in the ’90s — she refused. Harvey reportedly transported parts of the brain across the country in a cider box that he kept stashed under a beer cooler.
In 1985, he published a paper on Einstein’s brain, which alleged that it actually looked different from the average brain and therefore functioned differently. Later studies, however, have disproved these theories, though some researchers maintain that Harvey’s work was correct.
Meanwhile, Harvey lost his medical license for incompetency in 1988.
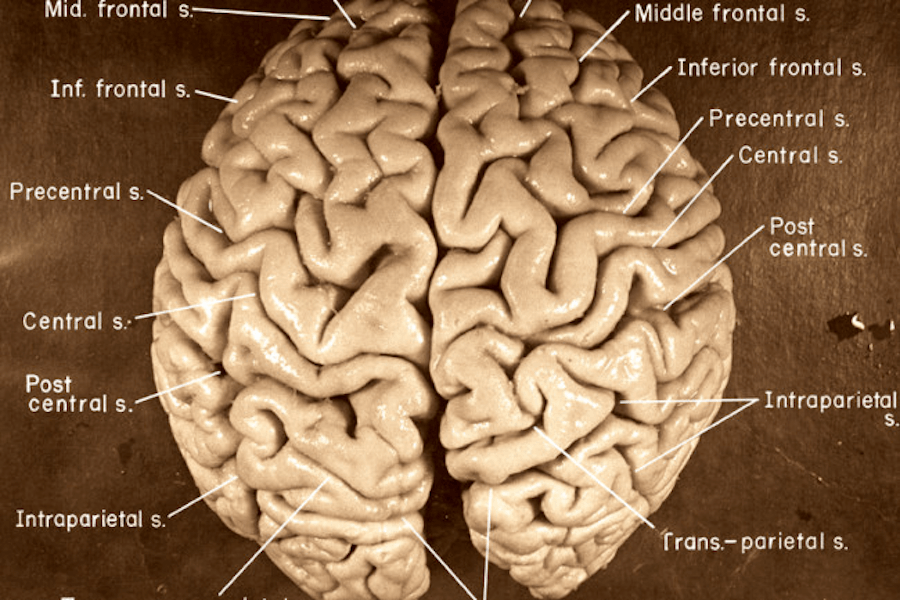
National Museum of Health and MedicineAlbert Einstein’s brain prior to its dissection in 1955.
Perhaps the case of Einstein’s brain can be summed up in this quote he once scrawled across the blackboard of his Princeton University office: “Not everything that counts can be counted, and not everything that can be counted counts.”
In addition to his charming legacy of childlike wonder and immense intelligence, Einstein has left the very tool behind his genius. These days, Einstein’s genius can be viewed at Philadelphia’s Mütter Museum.
After learning about the cause of Albert Einstein’s death, read about the fascinating story behind Albert Einstein’s iconic tongue photo. Then, learn about why Albert Einstein turned down the presidency of Israel.





